What is BIM-Building Information Modeling?
BIM, Building Information Modelling is a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a facility. A building information modelling is a shared knowledge resource for information about a facility forming a reliable basis for decisions during its life cycle; defined as existing from earliest conception to demolition.
BIM (Building Information Modelling) can also be a collaborative working methodology between designers, builders, architects, installers, manufacturers, and other agents involved in the construction process for the creation and management of a construction project from start to finish.

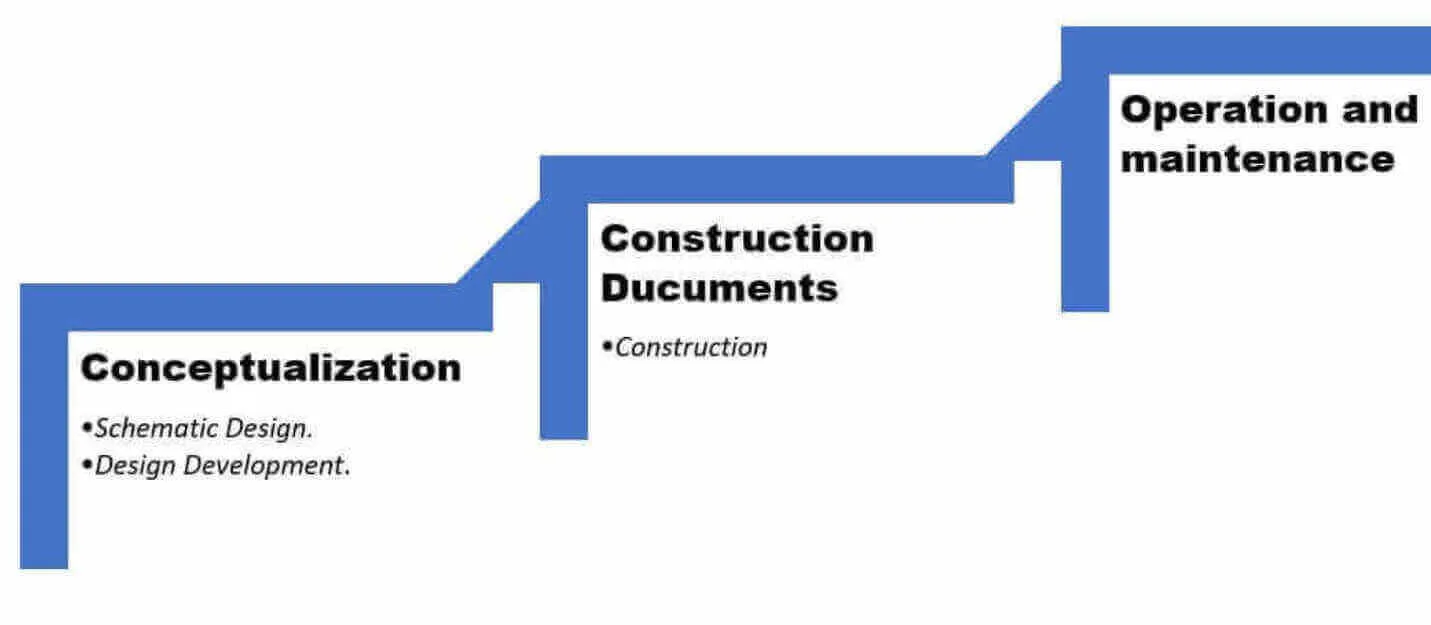
The processes/stages/phases involved in Building Information Modelling.
-
Conceptualization
In this stage the designer works with the client to develop a preliminary concept for the infrastructure, key areas to note by the designer is the indented use of the building, site analysis and other relevant information to develop a basic understanding of the project’s scope and requirements. in this stage, developing sketches, drawings and 3d models may be required to illustrate the initial design concept.
-
Schematic Design
Here, the designer takes the initial concept from the previous stage and develop a rough sketch of the infrastructure project, this stage simply involves creation of 3D models choosing from the diverse BIM software, which allows the designer to visualize the overall layout of the infrastructure and locate key elements such as walls, doors, windows, lintels and structural element and or so mechanical and electrical systems in this stage.
-
Design development
In this stage, the designer refines the design developed in the previous stage by adding more details and finalizing the building form, structure, and systems. this stay may also require creation of multiple 3D models to explore different design options, as well as the creation of detailed drawings and specifications for the building construction. Here the Building Information Modelling software can be used to evaluate environmental impacts of different materials and systems and optimize the design for energy efficiency.
-
Construction documentation
In this stage, the designer creates detailed construction documents that includes drawing specifications, schedules and instructions for the contractor to follow during the next stage. This stage basically involves the creation of detailed drawings, schedules and list of materials as well as generation of 3D models to help ensure that all elements are encountered for the construction process.
-
Construction
In this stage, all the specifications, schedules, and instructions provided by the designer are followed and the project is implemented on ground based on the details provided. Regular inspection is usually employed to make sure that all elements in the drawing are provided and should there be a variation, then its handled accordingly.
-
Operation and maintenance
In the final stage, the construction process is complete including all the details from the drawings and the facility is handed to the owner who is responsible for usage and maintenance of the building. During this stage, the Building information models can be used to facilitate maintenance and repairs as well as track energy usage and operational data. This information can be used to optimize the building performance over time, ensuring that it remains energy efficient and cost effective.
Types of Building Information Modeling.
-
3D BIM
This is the very most common building information model type known, because it only involves the modeling of the virtual building environment, this model can be used to visualize the overall layout of the project and to detect any conflict or issue that may arise during the construction process. 3D BIM is typically used during the early stages of the design process to develop a conceptual design for the project.
-
4D BIM
4D BIM includes time as an additional dimension. in addition to 3D model of the building, 4D BIM also includes a construction schedule that is integrated into the model. this allows stakeholders to visualize the construction process in a more detailed and comprehensive way, and to detect any potential scheduling conflict or delays. This BIM is typically used during the construction documentation stage of the project.
-
5D BIM
This BIM includes details of 3D, 4D BIM and additional dimensions such as costs. in addition to 3D models of the building and the construction schedule, 5D BIM also includes a detailed cost estimate for the project. As off course this allows stake holders to better understand cost implications of different designs and timeline. 5D BIM is used during the 3rd and the 4th stages of the BIM process.
-
6D BIM
Additional component to compose the 6D BIM is addition of data related to the building’s sustainability and environmental impacts. 6D BIM in addition to 3D, 4D, and 5D, it includes data related to energy usage, material selection and other factors that affect the building environmental performance. this allows stake holders to make more informed decisions about the building’s sustainability and to track its performance over time. 6D BIM is used during the operation and maintenance stage of the project.
-
7D BIM
7D BIM includes additional data related to the building’s facility management and operations. in addition to 3D models, the construction schedule, the cost estimate, and the sustainability data, 7D BIM also includes data related to maintenance schedules, repair history, and other factors that affect the building’s ongoing operations. this allows stake holders to more effectively manage the building’s ongoing maintenance and to optimize its performance over time. its used during the operational and maintenance stage of the project.