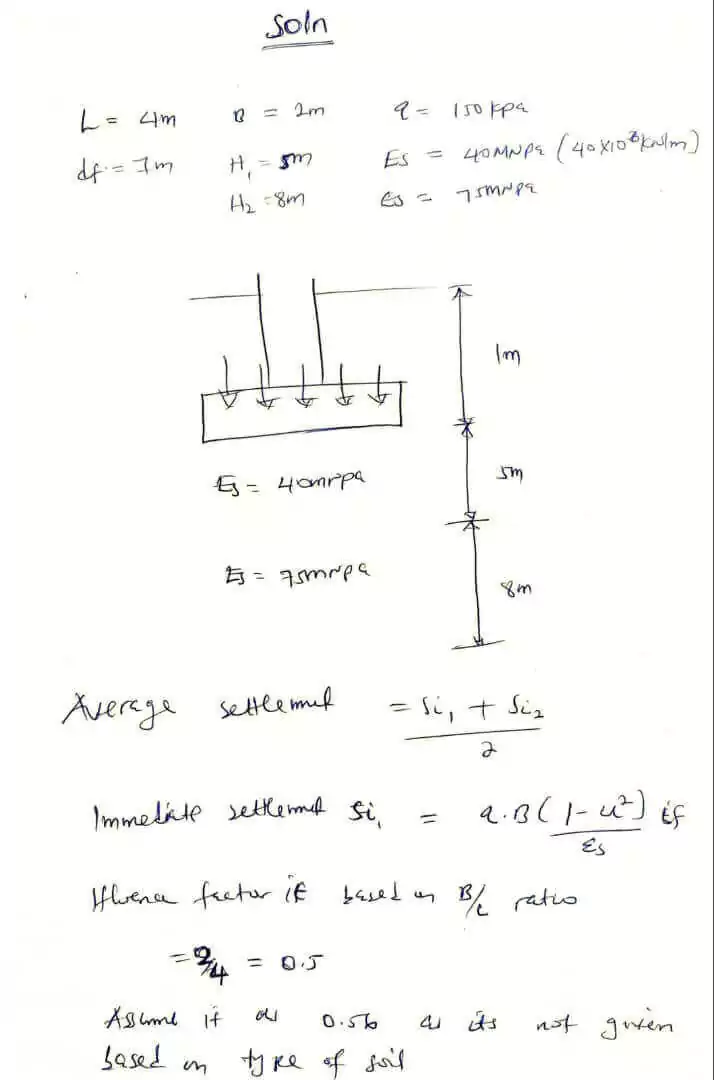
Question
A foundation 4m x 2m carries a uniform pressure of 200kPa at a depth of 1m in a layer of saturated clay 11m deep and underlain by a hard stratum. If undrained elastic modulus, Es for the clay is 45MPa, determine the average value of immediate settlement under the foundation.
Solution to A foundation 4m…



Immediate settlement
The load causes instant changes in the soil stresses, and reduces soil voids, as soon as the load is applied.
What causes soil settlement?
Geotechnical settlement is typically the result of loading
(from a building or vehicles moving along on a road, for example) exceeding the ground’s bearing capacity.
Due to site ground pressures, pore water pressure increases and then dissipates,
causing consolidation settlement, where the soil beneath the structure moves vertically and horizontally.
Weak and poorly compacted soils are particularly vulnerable.
Soil settlement can be caused by other factors too,
such as changes in soil moisture content, for example, saturated cohesive soils may soften or drier cohesive soils may shrink.
Deep excavations and tunneling, plus the collapse of naturally occurring voids or abandoned mine workings,
are also key factors in causing different types of settlement.
Settlement occurs immediately after a load is applied or take years, depending on the underlying soil conditions
Geotechnical engineers often carry out settlement analysis prior to construction to analyze the ground conditions
and recommend foundation solutions for preventing settlement in the future.