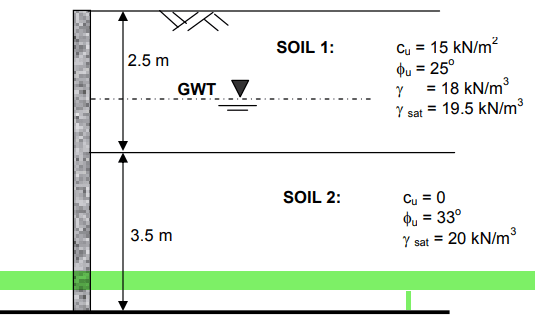
Question For the smooth vertical wall shown in the figure 1 below. determine the total active thrust on the wall and the position where it acts. ground water level is at a depth of 1.5m Solution See Related Active Thrust Active thrust in retaining walls refers to the horizontal force exerted by soil on a retaining wall when the wall allows some lateral movement. As the wall moves slightly away from the retained soil, the pressure exerted by the soil decreases compared to when the wall is stationary or constrained. Here’s a more detailed explanation: What is it? Active thrust (or active earth pressure) describes the pressure that soil exerts against a retaining wall when the wall moves away from the retained soil. . This movement leads to a reduction in the force or pressure exerted by the soil compared to at-rest conditions How does it occur? When designers create a retaining wall to allow some degree of movement or rotation away from the retained soil, the soil’s pressure decreases. This condition is called “active,” in contrast to “at-rest” (when the wall doesn’t move) or “passive” (when the wall moves towards the soil, causing increased pressure) As the wall moves, the soil behind it shifts and adjusts, resulting in a reduction in the earth pressure against the wall. This allows the soil to reach an equilibrium state with lower lateral pressure. Why is it important? Understanding active thrust is crucial for designing retaining walls that can handle expected forces without failing. By allowing the wall to move slightly, engineers can design more efficient structures that are less likely to be overstressed by soil pressure. Implications for Retaining Wall Design When designing for active thrust, engineers typically calculate the active earth pressure using specific theories and formulas (like Rankine or Coulomb’s theories) to determine the force acting on the wall. Designers typically factor in the small movement of the wall that’s necessary to reach active conditions to ensure stability and safety....